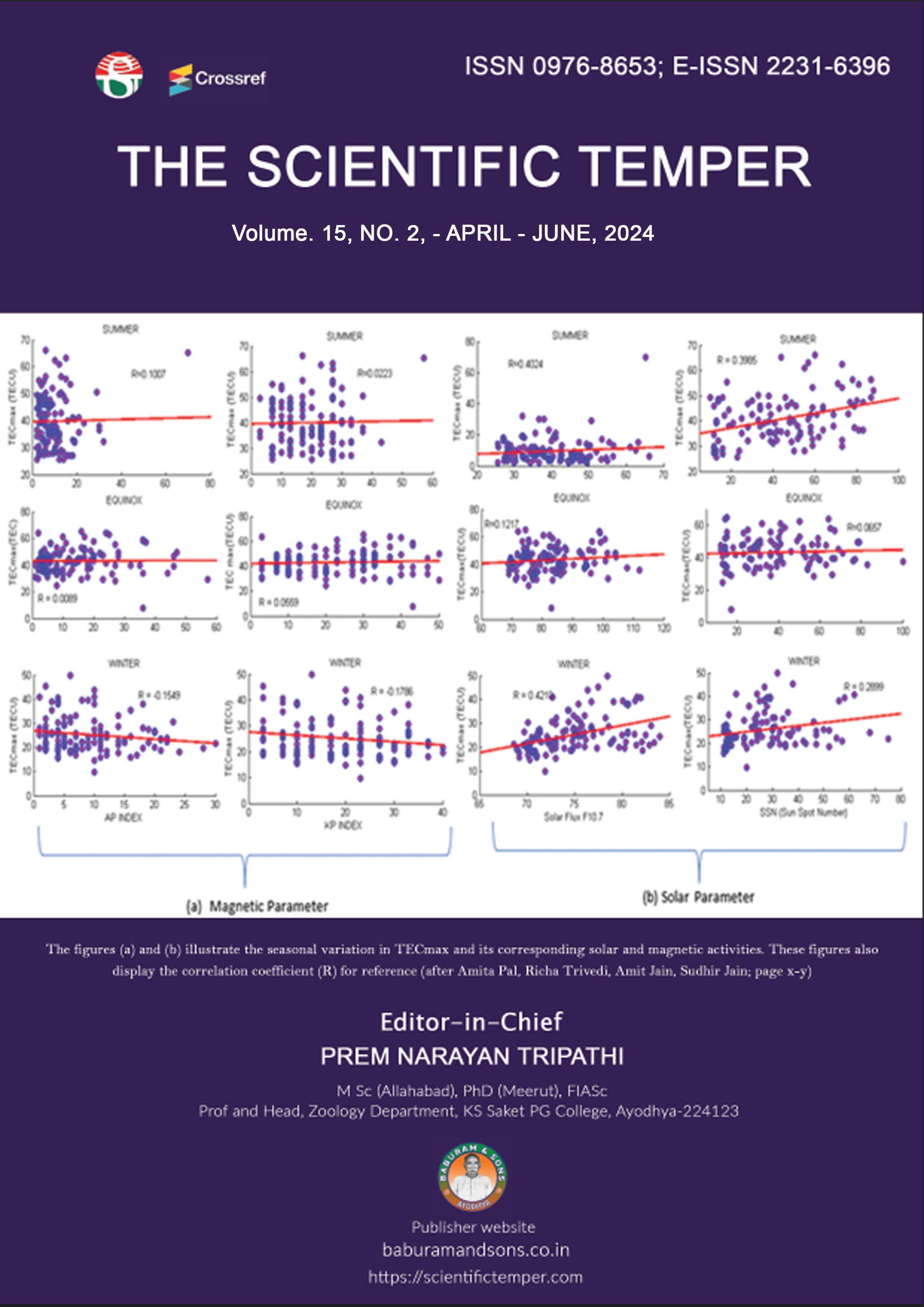
Diurnal and seasonal variation of GPS-TEC during a low solar activity period at EIA region (Bhopal)
Downloads
Published
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.58414/SCIENTIFICTEMPER.2024.15.2.16Keywords:
Keywords: Total Electron Content (TEC); Equatorial Ionization Anomaly (EIA); Global Positioning System (GPS); Solar Indices; Electron Electrojet (EEJ).Dimensions Badge
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The Scientific Temper

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The ionosphere near the equatorial ionization anomaly crest region in the Indian ionospheric sector was studied from May 2016 to April 2017, a solar minimum period. Total electron content (TEC) recorded using the multiple frequency GPS receivers at Bhopal (23.2° N, 77.4° E & MLAT 14.2° N) is used for the study. The diurnal variation shows that the day minimum in TEC is attained around 06:00 hours LT, and the day maximum occurs at about 16:00 hours LT. A similar diurnal pattern was observed in all months across various seasons. During the period of study, it was observed that Seasonal variation of TEC was minimal in winter, whereas highest during equinox and summer months. The variation of TECmax with EEJ shows a positive correlation between the parameters for all the months. The highest correlation (0.8398) was observed in January 2017, while it was lowest (0.4004) in March 2017 and the results were compared with earlier observations, and a possible mechanism was discussed.Abstract
How to Cite
Downloads
Similar Articles
- Ganga Gudi, Mallamma V Reddy, Hanumanthappa M, Enhancing Kannada text-to-speech and braille conversion with deep learning for the visually impaired , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 16 No. Spl-1 (2025): The Scientific Temper
- Goutam Mandal, Baibaswata Bhattacharjee, Biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using the young fruit of Borassus flabellifer: Characterization and photocatalytic removal of biohazardous safranin-O dye using solar irradiation , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 15 No. 02 (2024): The Scientific Temper
- Rajeshwar Mukherjee, Uday S. Dixit, Understanding cosmopsychism based on stochastic electrodynamics from the perspective of the Indian knowledge system , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 14 No. 03 (2023): The Scientific Temper
- V. Manikandabalaji, R. Sivakumar, V. Maniraj, A framework for diabetes diagnosis based on type-2 fuzzy semantic ontology approach , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 15 No. 03 (2024): The Scientific Temper
- Syed Amin Jameel, Abdul Rahim Mohamed Shanavas, Deep-Ultranet: Diabetic Retinopathy Grading System Using Ultra-Widefield Retinal Images , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 16 No. 12 (2025): The Scientific Temper
- Amita Gupta, A study of the scientific approach inherited in the Indian knowledge system (IKS) , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 15 No. 02 (2024): The Scientific Temper
- Bhavesh Parekh, Parthiv Patel, Unravelling Indianness in R.K. Narayan’s novels: A multidisciplinary exploration of culture, tradition and modernity , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 16 No. 03 (2025): The Scientific Temper
- Shaik Chanbasha, N. Jayakumar, N. Bupesh Kumar, A self-regulating optimization algorithm for locating and sizing a local power generation source for a radial structured distribution system in deregulated environment , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 15 No. 03 (2024): The Scientific Temper
- Rajesh Kumar Singh, Abhishek Kumar Mishra, Ramapati Mishra, Hand Gesture Identification for Improving Accuracy Using Convolutional Neural Network(CNN) , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 13 No. 02 (2022): The Scientific Temper
- Mohiyuddeen Hafzal, Management strategies for sustainable development goals: A roadmap to Viksit Bharat@2047 , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 16 No. Spl-1 (2025): The Scientific Temper
<< < 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 > >>
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.