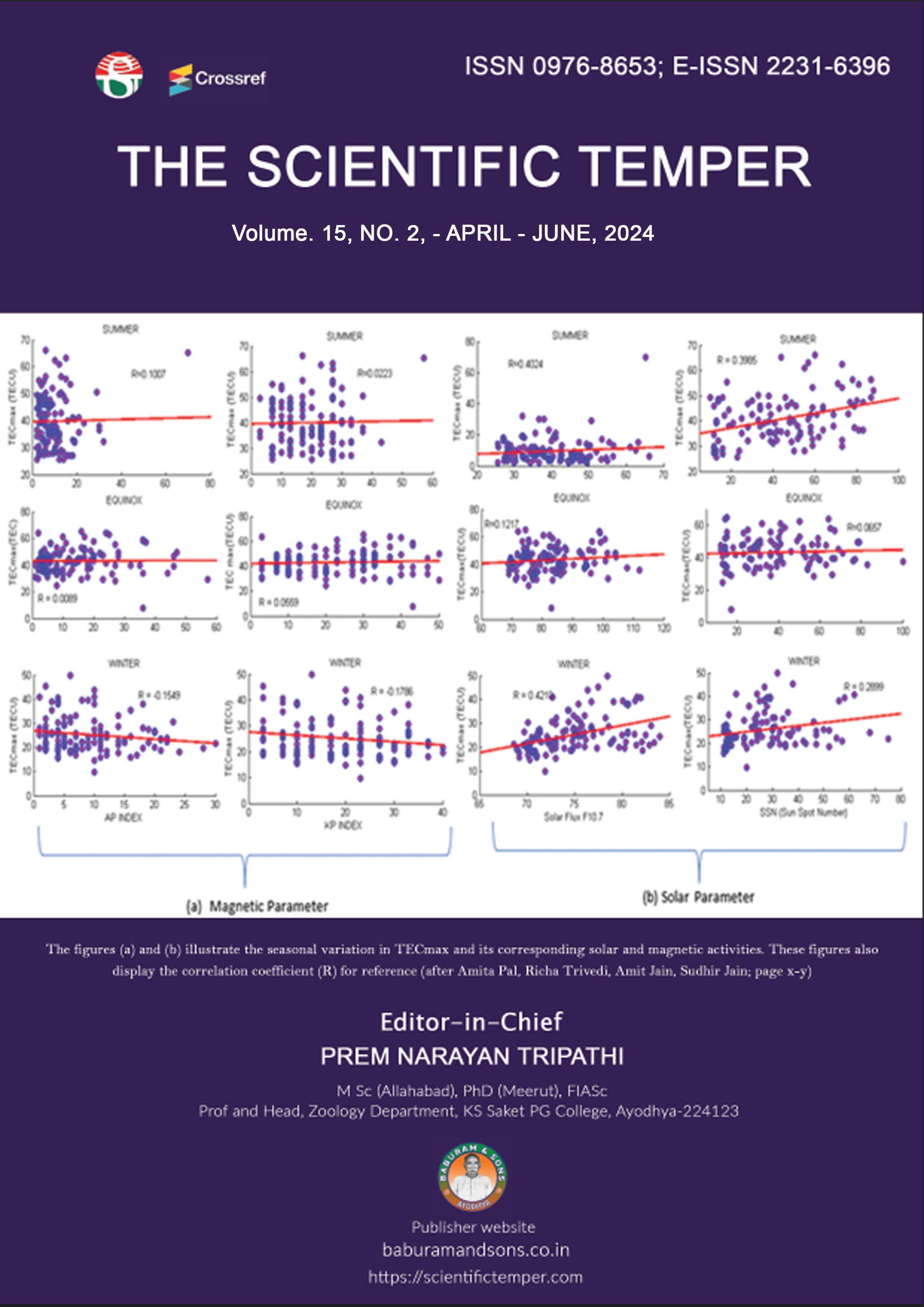
Diurnal and seasonal variation of GPS-TEC during a low solar activity period at EIA region (Bhopal)
Downloads
Published
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.58414/SCIENTIFICTEMPER.2024.15.2.16Keywords:
Keywords: Total Electron Content (TEC); Equatorial Ionization Anomaly (EIA); Global Positioning System (GPS); Solar Indices; Electron Electrojet (EEJ).Dimensions Badge
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The Scientific Temper

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The ionosphere near the equatorial ionization anomaly crest region in the Indian ionospheric sector was studied from May 2016 to April 2017, a solar minimum period. Total electron content (TEC) recorded using the multiple frequency GPS receivers at Bhopal (23.2° N, 77.4° E & MLAT 14.2° N) is used for the study. The diurnal variation shows that the day minimum in TEC is attained around 06:00 hours LT, and the day maximum occurs at about 16:00 hours LT. A similar diurnal pattern was observed in all months across various seasons. During the period of study, it was observed that Seasonal variation of TEC was minimal in winter, whereas highest during equinox and summer months. The variation of TECmax with EEJ shows a positive correlation between the parameters for all the months. The highest correlation (0.8398) was observed in January 2017, while it was lowest (0.4004) in March 2017 and the results were compared with earlier observations, and a possible mechanism was discussed.Abstract
How to Cite
Downloads
Similar Articles
- Elangovan G. Reddy, Anjana Devi V, Subedha V, Tirapathi Reddy B, Viswanathan R, A smart irrigation monitoring service using wireless sensor networks , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 14 No. 04 (2023): The Scientific Temper
- Deepa S, Sripriya T, Radhika M, Jeneetha J. J, Experimental evaluation of artificial intelligence assisted heart disease prediction using deep learning principle , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 14 No. 04 (2023): The Scientific Temper
- R. Kalaiselvi, P. Meenakshi Sundaram, Unified framework for sybil attack detection in mobile ad hoc networks using machine learning approach , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 16 No. 02 (2025): The Scientific Temper
- Arvind Kumar Tiwari, STABILITY IN THE EQUILIBRIUM POSITION OF AN EXTENSIBLE CABLE-CONNECTED TWO SATELLITE SYSTEM UNDER PERTURBATIVE FORCE IN CIRCULAR ORBIT , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 9 No. 1&2 (2018): The Scientific Temper
- A. R. Jasmine Begum, M. Parveen, S. Latha, IoT based home automation with energy management , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 14 No. 03 (2023): The Scientific Temper
- Suprabha Amit Kshatriya, Jaymin K Bhalani, Fire and smoke detection with high accuracy using YOLOv5 , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 16 No. 06 (2025): The Scientific Temper
- Aditi Sahariya, Chellapilla Bharadwaj, Iwuala Emmanuel, Afroz Alam, Phytochemical Profiling and GCMS Analysis of Two Different Varieties of Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Under Fluoride Stress , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 12 No. 1&2 (2021): The Scientific Temper
- Swetadri Samadder, Analyzing the impact of COVID-19 on global stock markets: An international comparative analysis , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 15 No. 01 (2024): The Scientific Temper
- Chirag Darji, Rajesh Chauhan, Views of undergraduates on Vikshit Bharat@2047 , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 15 No. spl-2 (2024): The Scientific Temper
- Neha Verma, Beyond likes & clicks: Empowering role of social media marketing in value creation , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 15 No. 01 (2024): The Scientific Temper
<< < 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 > >>
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.