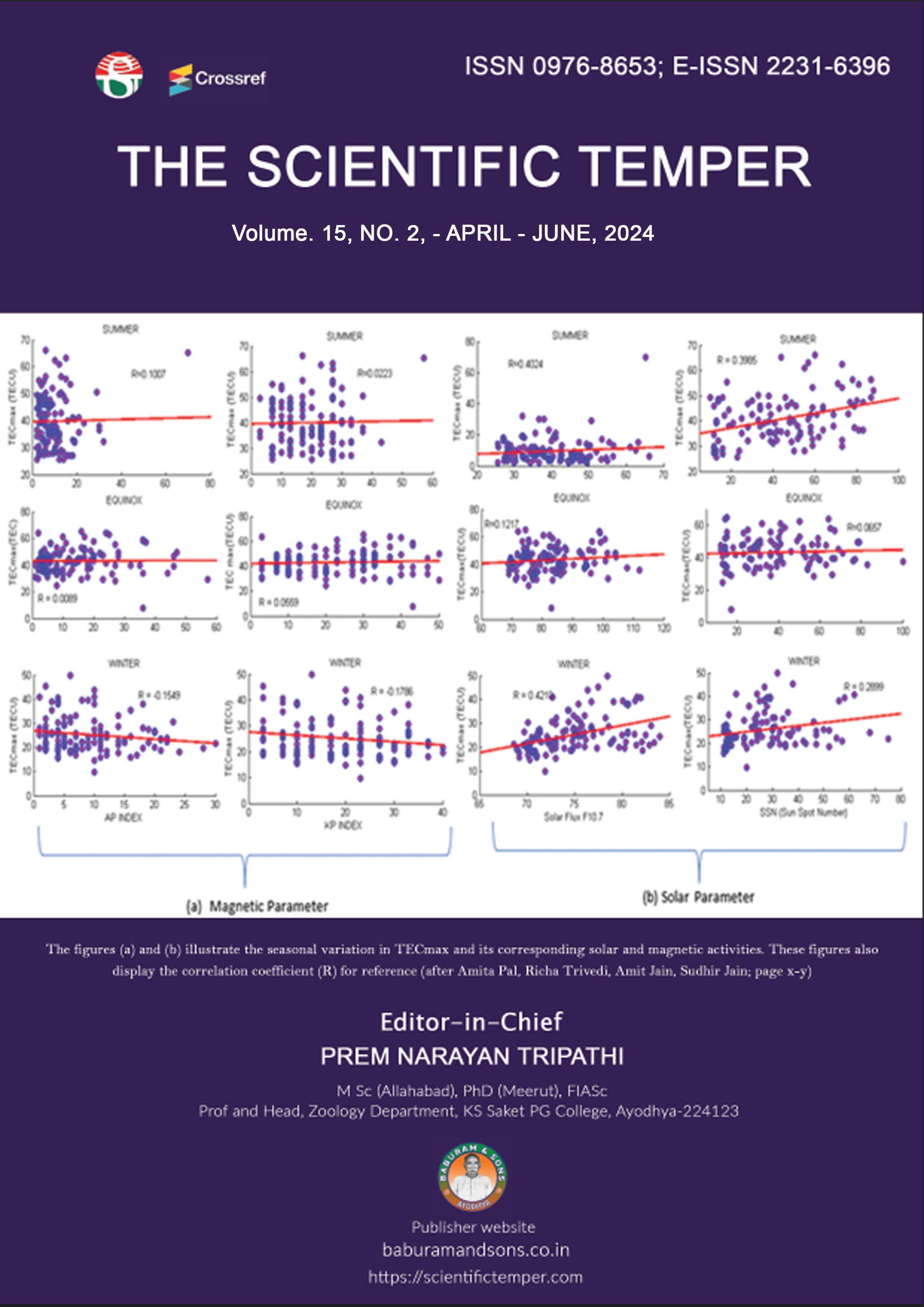
Diurnal and seasonal variation of GPS-TEC during a low solar activity period at EIA region (Bhopal)
Downloads
Published
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.58414/SCIENTIFICTEMPER.2024.15.2.16Keywords:
Keywords: Total Electron Content (TEC); Equatorial Ionization Anomaly (EIA); Global Positioning System (GPS); Solar Indices; Electron Electrojet (EEJ).Dimensions Badge
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The Scientific Temper

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The ionosphere near the equatorial ionization anomaly crest region in the Indian ionospheric sector was studied from May 2016 to April 2017, a solar minimum period. Total electron content (TEC) recorded using the multiple frequency GPS receivers at Bhopal (23.2° N, 77.4° E & MLAT 14.2° N) is used for the study. The diurnal variation shows that the day minimum in TEC is attained around 06:00 hours LT, and the day maximum occurs at about 16:00 hours LT. A similar diurnal pattern was observed in all months across various seasons. During the period of study, it was observed that Seasonal variation of TEC was minimal in winter, whereas highest during equinox and summer months. The variation of TECmax with EEJ shows a positive correlation between the parameters for all the months. The highest correlation (0.8398) was observed in January 2017, while it was lowest (0.4004) in March 2017 and the results were compared with earlier observations, and a possible mechanism was discussed.Abstract
How to Cite
Downloads
Similar Articles
- M. Monika, J. Merline Vinotha, Optimization of a Lean Vendor–Buyer Supply Chain Model under Neutrosophic Fuzzy Environment with Transportation, Loading, and Unloading Considerations , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 16 No. 10 (2025): The Scientific Temper
- M. Deepika, I. Antonitte Vinoline, The Impact of ERP Integration and Preservation Technology on Profit Optimization in Inventory Systems with Shortages and Deterioration , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 16 No. 09 (2025): The Scientific Temper
- Abhishek K Pandey, Amrita Sahu, Ajay K Harit, Manoj Singh, Nutritional composition of the wild variety of edible vegetables consumed by the tribal community of Raipur, Chhattisgarh, India , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 14 No. 01 (2023): The Scientific Temper
- Muthuvel Balasubramanian, Jonnakuti V. G. Rama Rao, Surya C. P. R. Sanaboina, Vavilala Venkatesh, Amalodbhavi Sanaboina, Tracking and control of power oscillation dampings in transmission lines using PV STATCOM , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 14 No. 03 (2023): The Scientific Temper
- Jonnakuti V. G. Rama Rao, Muthuvel Balasubramanian, Chaladi S. Gangabhavani, Mutyala A. Devi, Kona D. Devi, A TLBO algorithm-based optimal sizing in a standalone hybrid renewable energy system , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 14 No. 03 (2023): The Scientific Temper
- N Archana, R Aravind Babu, Fault-tolerant reconfigurable second-life battery system using cascaded DC- DC converter , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 14 No. 01 (2023): The Scientific Temper
- U. Johns Praveena, J. Merline Vinotha, Multi-objective Solid Green Trans-shipment Problem for Cold Chain Logistics under Fuzzy Environment , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 16 No. 12 (2025): The Scientific Temper
- Meera Yadav, F. D. Yadav, Effect of TLCV on Metabolic Parameter and Yield of Tomato , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 11 No. 1&2 (2020): The Scientific Temper
- Deepika M, Antonitte Vinoline I, An integrated inventory system for profit maximization considering partial demand satisfaction , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 16 No. 08 (2025): The Scientific Temper
- Anurag Tripathi, Shri Prakash, Prem Narayan Tripathi, Impact of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) on the Nervous System: A Critical Review , The Scientific Temper: Vol. 11 No. 1&2 (2020): The Scientific Temper
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.